2024 Quarterly Results
Noevember 2024
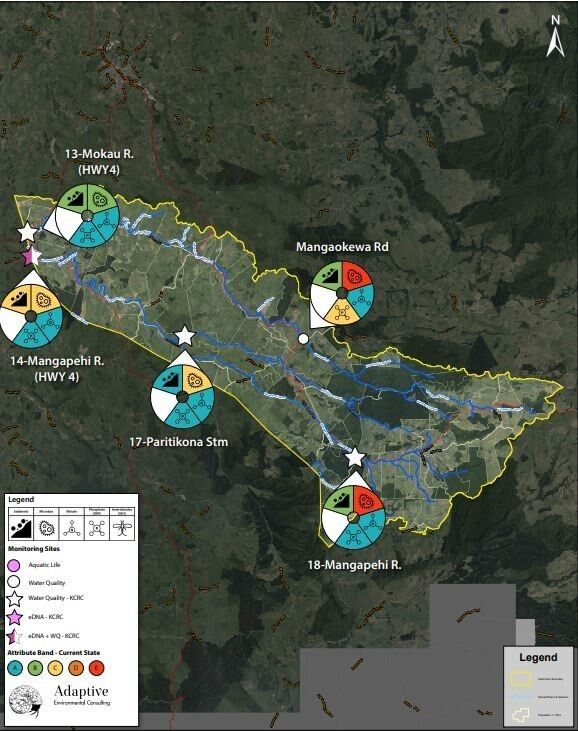
Water quality was Fair. E. coli and suspended sediment were elevated at all sites, while nutrient indicators were low at most sites.
E. coli concentrations were elevated at all sites (between 370 and 670) and fell above the recommend health limits for swimming (540) at one site, 18-Mangapehi river. E. coli concentrations were lowest at 13-Mokau river and highest at 18-Mangapehi river. Nitrate concentrations were low at all sites, falling well below ecological toxicity levels (2.4 mg/L). Nitrates were lowest at 13-Mokau R. HWY 4 (0.33 mg/L) and highest at 18-Mangapehi River (0.64 mg/L). Ammonia concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 0.03 mg/L). Dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) concentrations were low at two sites (≤ 0.43 mg/L) but were slightly elevated at 18-Mangapehi river (0.67 mg/L). DIN concentrations greater than 0.5 mg/L can cause ecological impacts like excessive growth of algae and aquatic plants, and loss of sensitive species. Dissolved reactive phosphorus concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 0.010 mg/L). Water clarity was low at all sites (between 0.60 and 1.10 m), relative to the national bottom line (1.34 m).
Sample Collection Date: 19th November
Mokau River – Summary of water quality collected at 15 sites across the Mokau River catchment on 19th November 2024
E. coli and suspended sediment were elevated across most sites and a third of all sites had elevated concentrations of dissolved inorganic nitrogen. While dissolved reactive phosphorus (DRP) was generally low, very high DRP concentrations were recorded at several locations.
E. coli: 73% of sites had elevated concentrations (between 610 and 1,500), 20% (3 sites) had slightly elevated concentrations (between 370 and 470), while only 7% (1 site) had a low concentration (≤ 110). Nitrate and Ammonia: 100% of sites were well below toxicity levels. Nitrate range (0.13 – 0.80 mg/L); Ammonia range (<0.005 - 0.05). Dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN): 67% of sites had low concentrations (≤ 0.46 mg/L) and 33% were slightly elevating, falling above the ecological impact threshold of 0.5 mg/L (between 0.54 and 0.81 mg/L). The highest DIN concentration recorded across the Mokau River catchment was 0.81 mg/L. Dissolved reactive phosphorus: 73% of sites had low concentrations (between <0.002 to 0.010 mg/L), 7% (1 site) was slightly elevated (0.017 mg/L) and 20% (3 sites) had very high concentrations (between 0.019 and 0.065 mg/L). Water clarity: 13% (2 sites) had good water clarity (A or B band), 13% (2 sites) had reduced water clarity (C band) and the remaining 73% had poor water clarity (D band). Bands for each site relate to the national bottom line (NBL) for water clarity and are dependent on landscape characteristics including geology, climate and elevation. The NBL for Mokau River’s monitoring sites are either 1.34 m or 0.61 m, dependant on the local landscape characteristics.
August 2024
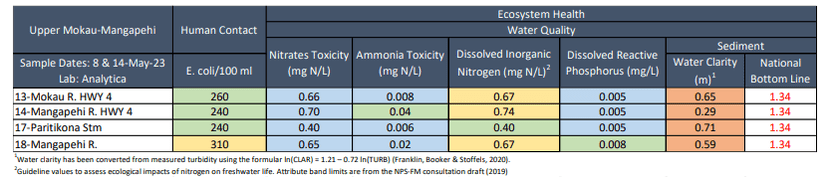
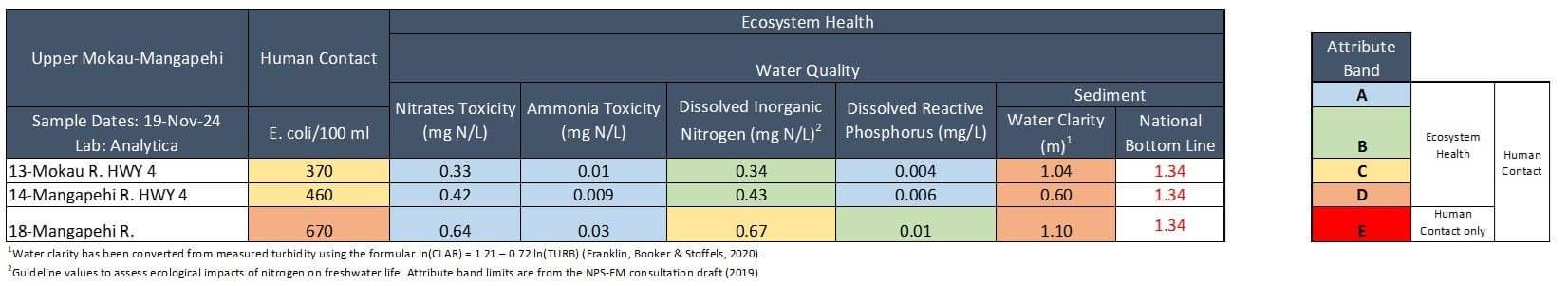
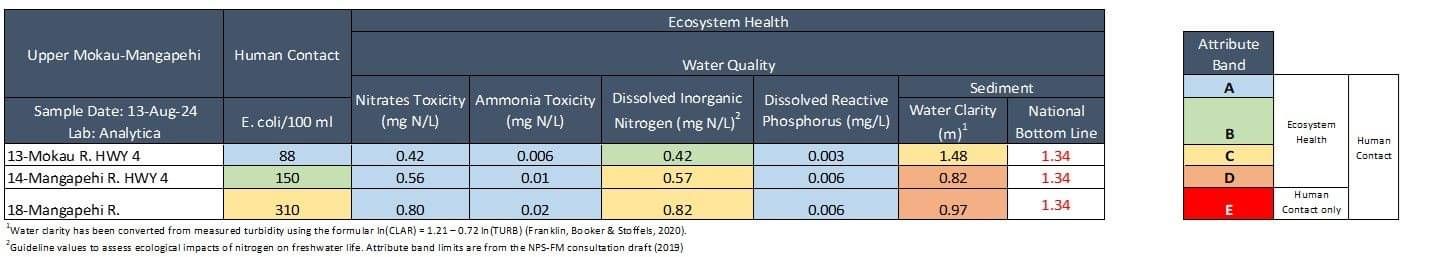
Water quality was Fair. E. coli and dissolved inorganic nitrogen were slightly elevated at two sites and water clarity was low at all sites.
E. coli concentrations were low at two sites (≤ 150) and slightly elevated at 18-Mangapehi River (310). All sites fell well within recommend health limits for swimming (540). Nitrate concentrations were low at all sites, well below ecological toxicity levels (2.4 mg/L). Nitrates were lowest at 13-Mokau R. HWY 4 (0.42 mg/L) and highest at 18-Mangapehi River (0.80 mg/L). Ammonia concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 0.02 mg/L). Dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) concentrations were low at 13-Mokau River (0.42 mg/L) but was slightly elevated at the other two sites (≥ 0.57 mg/L). DIN concentrations greater than 0.5 mg/L can cause ecological impacts like excessive growth of algae and aquatic plants, and loss of sensitive species. Dissolved reactive phosphorus concentrations were very low at all sites (≤ 0.006 mg/L). Water clarity was slightly low at 13-Mokau River (1.48 m) and poor at the other two sites (≤ 0.97 m), relative to the national bottom line (1.34 m).
Sample Collection Days: 13th August 2024
Mokau River – Summary of water quality collected at 15 sites across the Mokau River catchment on 13th August 2024
E. coli, ammonia and dissolved reactive phosphorus were low at most sites. The key contaminants were suspended sediment and nitrate.
E. coli: 73% of all sites had low concentrations (≤210), while 27% (4 sites) had slightly elevated concentrations (between 310 to 410). Nitrate and Ammonia: 100% of sites were well below toxicity levels. Nitrate range (0.2 – 0.92 mg/L); Ammonia range (<0.005 - 0.03). Dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN): 53% of sites had low concentrations (≤0.47 mg/L) and 47% fell above the ecological impact threshold of 0.5 mg/L. The highest DIN concentration was 0.93 mg/L. Dissolved reactive phosphorus: 93% of sites had low concentrations (between <0.002 to 0.009 mg/L), 7% (1 site) had slightly elevated concentrations 0.012 mg/L. Water clarity: 27% (4 sites) had good water clarity (A or B band), 7% (1 site) had reduced water clarity (C band) and the remaining 67% had poor water clarity (D band). Bands for each site relate to the national bottom line (NBL) for water clarity and are dependent on landscape characteristics including geology, climate and elevation. The NBL for Mokau River’s monitoring sites are either 1.34 m or 0.61 m, dependant on the local landscape characteristics.
May 2024
Overall, water quality was Good, only dissolved inorganic nitrogen was slightly elevated at one site and water clarity was slightly low at another site.
E. coli concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 140), falling well within recommend health limits for swimming (540). Nitrate concentrations were low at all sites and well below ecological toxicity levels (2.4 mg/L). Nitrates were lowest at 13-Mokau R. HWY 4 (0.25 mg/L) and highest at 18-Mangapehi River (0.58 mg/L). Ammonia concentrations were very low at all sites (≤ 0.02 mg/L). Dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations were low at 2 sites (≤ 0.38 mg/L) but slightly elevated at 18-Mangapehi River (0.6 mg/L), potentially promoting excessive growth of algae, aquatic plants and impacting sensitive aquatic species at this site. Dissolved reactive phosphorus concentrations were very low at all sites (≤ 0.005 mg/L). Water clarity was excellent at 18-Mangapehi River (2.20 m), good at 13-Mokau River (1.64 m) and low at 14-Mangapehi River (1.48 m), relative to the national bottom line (1.34 m).
Collection day: 14th May 2024
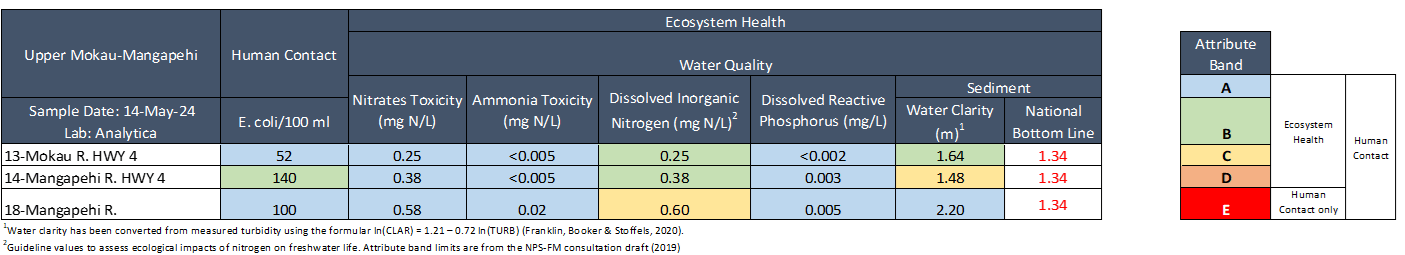
Mokau River – Summary of water quality collected at 15 sites across the Mokau River catchment May 2024
E. coli and Nutrients (nitrate, ammonia and dissolved reactive phosphorus) were low at most sites. The key contaminant was suspended sediment.
E. coli: 93% of all sites had low concentrations (≤240) and 7% (1 site) had elevated concentrations (510). Nitrate and Ammonia: 100% of sites were well below toxicity levels. Nitrate range (0.15 – 0.79 mg/L); Ammonia range (<0.005 - 0.02). Dissolved inorganic nitrogen: 73% of sites had low concentrations (≤0.44 mg/L) and 27% (4 sites) fell above the ecological impact threshold of 0.5 mg/L with the highest concentration being 0.79 mg/L. Dissolved reactive phosphorus: 100% of sites had low concentrations (between <0.002 - 0.008 mg/L). Water clarity: 60% of sites had good water clarity (A or B band), 20% (3 sites) had reduced water clarity (C band) and the remaining 20% had poor water clarity (D band). Bands for each site relate to the national bottom line (NBL) for water clarity and are dependent on landscape characteristics including geology, climate and elevation. The NBL for Mokau River’s monitoring sites are either 1.34 m or 0.61 m, dependant the local landscape characteristics.
February 2024
Overall, water quality Excellent!
E. coli concentrations was low at all sites (260) and well within recommend health limits for swimming (540). Nitrate concentrations were low at all sites and well below ecological toxicity levels (2.4 mg/L). Nitrates were lowest at 13-Mokau R. HWY 4 (0.08 mg/L) and highest at 18-Mangapehi River (0.34 mg/L). Ammonia concentrations were very low at all sites (< 0.005 mg/L). Dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 0.34 mg/L). Dissolved reactive phosphorus concentrations were very low at all sites (≤ 0.003 mg/L). Water clarity was excellent at 13-Mokau River and 18-Mangapehi River (≥ 1.79 m) and good at 14-Mangapehi River 1.56 m), relative to the national bottom line (1.34 m).
Collection date: 22nd & 28th February 2024
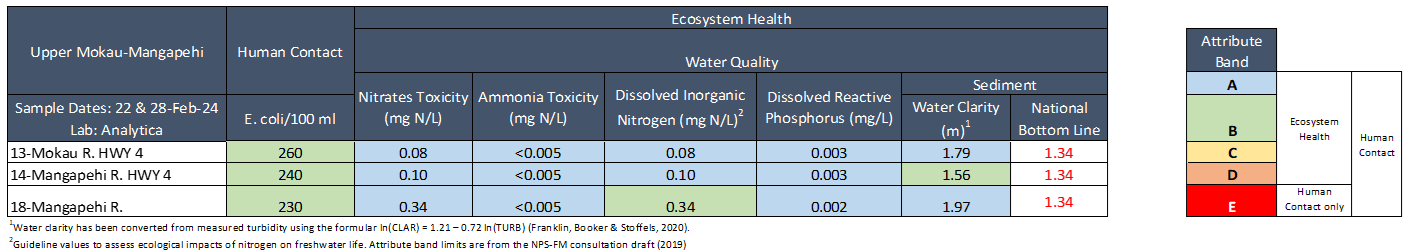
Mokau River – Summary of water quality collected at 15 sites across the Mokau River catchment February 2024
Nutrient concentrations (nitrate, ammonia and dissolved reactive phosphorus) were low at most sites. Key contaminants were E. coli and suspended sediment.
E. coli: 60% of all sites had low concentrations (≤260) and 40% had slightly elevated concentrations (between 300 - 450). Nitrate and Ammonia: 100% of sites were well below toxicity levels. Nitrate range (0.04 – 0.53 mg/L); Ammonia range (<0.005 - 0.03). Dissolved inorganic nitrogen: 87% of sites had low concentrations (≤0.4 mg/L) and 13% (2 sites) fell above the ecological impact threshold of 0.5 mg/L with the highest concentration being 0.54 mg/L. Dissolved reactive phosphorus: 100% of sites had low concentrations (between <0.002 - 0.01 mg/L). Water clarity: 53% of sites had good water clarity (A or B band), 13% (2 sites) had reduced water clarity (C band) and 33% of sites had poor water clarity (D band). Bands for each site relate to the national bottom line (NBL) for water clarity and are dependent on landscape characteristics including geology, climate and elevation. The NBL for Mokau River’s monitoring sites are either 1.34 m or 0.61 m, dependant the local landscape characteristics.
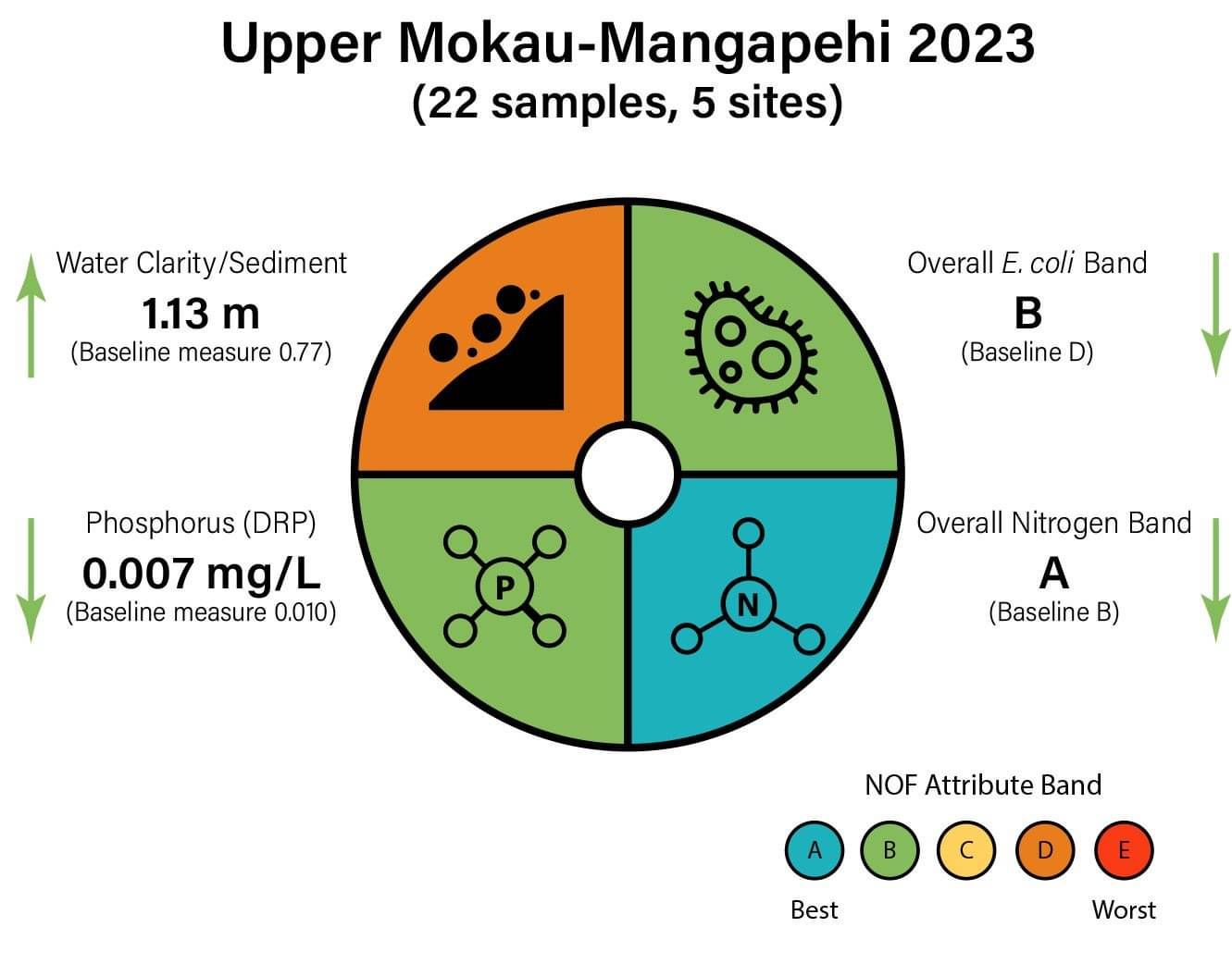
Water Quality Summary 2023
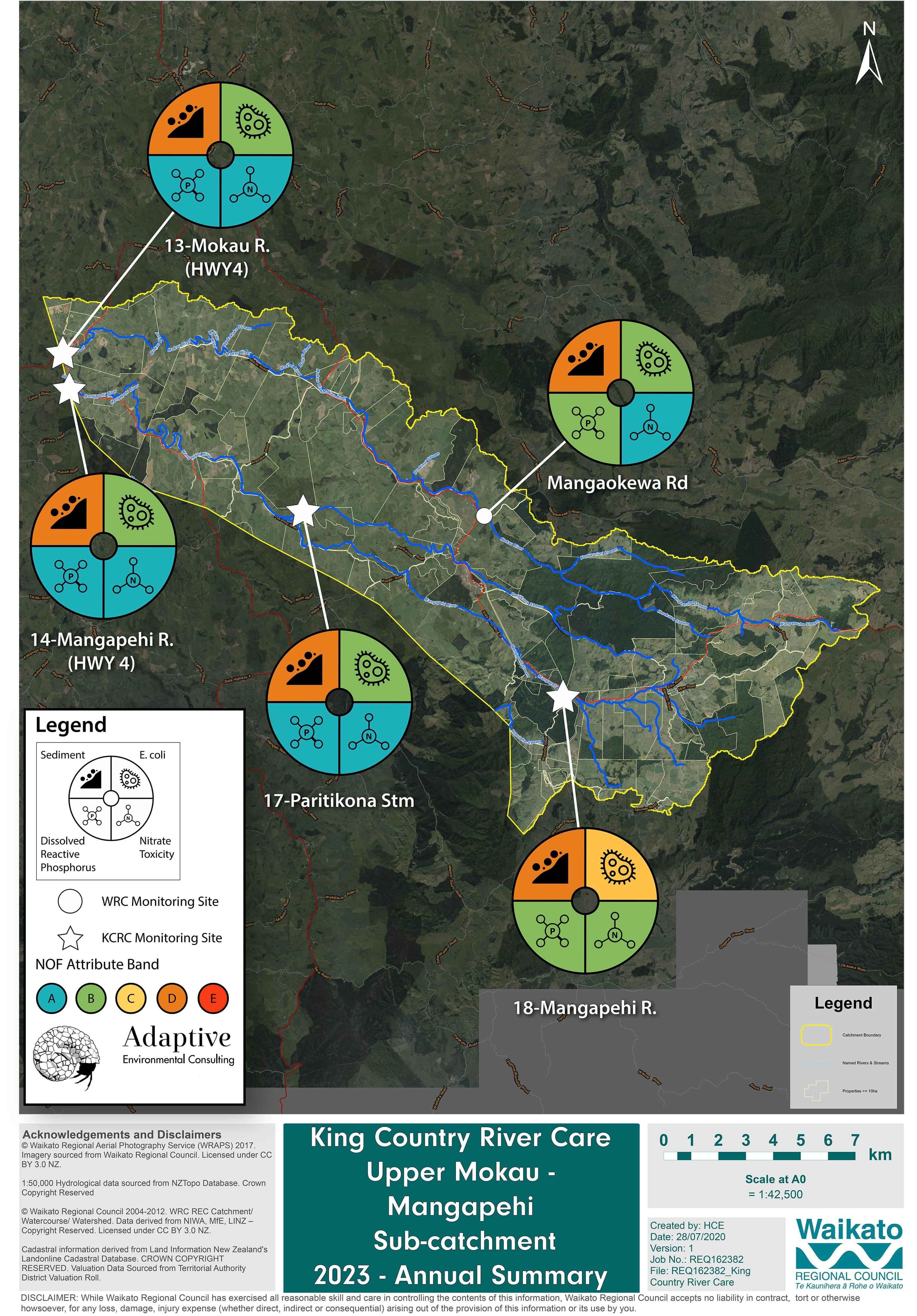
Water samples were collected from 5 stream and river sites across the Upper Mokau-Mangapehi catchment. Monitoring sites were located on Paritikona stream, Mangapehi River and the Mokau River. The below water quality dial summarises 22 individual samples collected across 5 sites, between January 2023 and December 2023.
Water clarity was poor, indicated elevated levels of suspended sediment, which impacts aquatic life. E. coli and dissolved reactive phosphorus (DRP) were low and nitrogen was very low, which supports human health (E. coli) and river health (nutrients). Water clarity did not meet national water quality standards, while all other attributes did meet national standards.
Arrows indicate an increase or decrease in values compared to the baseline. The baseline was calculated from 5 years of data collected by Waikato Regional Council at 5 sites, between 2015 and 2019. An increase in water clarity is positive for river health, while an increase in all other attributes may impair river health.
Aquatic Biodiversity Summary
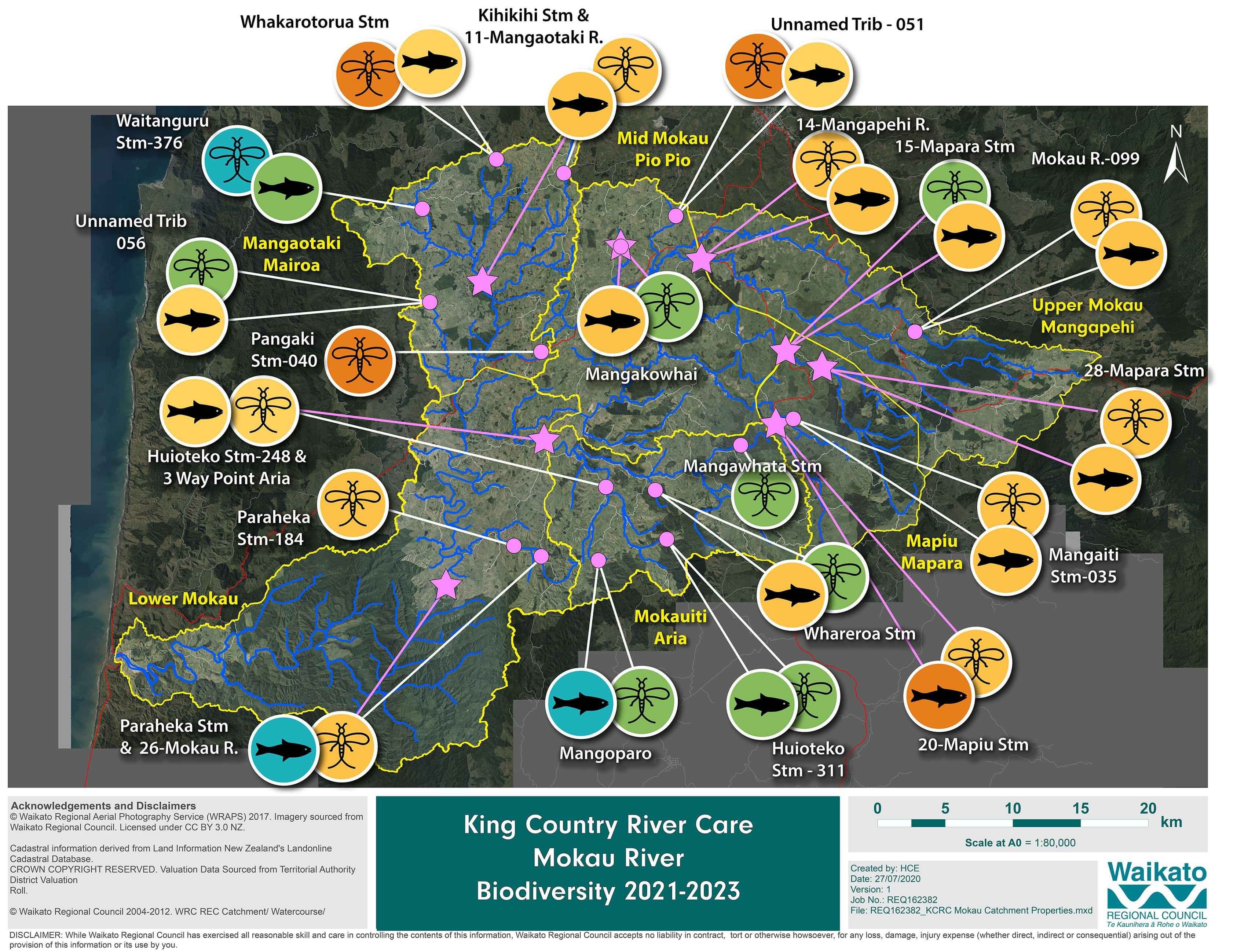
Biodiversity monitoring includes eDNA, collected by KCRC, and traditional biodiversity monitoring techniques (netting of freshwater invertebrates and netting and electrofishing of freshwater fish), by Waikato Regional Council (WRC). eDNA sampling has been done by KCRC, in autumn and winter in 2021, 2022 and 2023. WRC monitors most sites every 1 to 2 years, between November and March. If more than one results is available for any single monitoring location the results for that site are averaged across years.
Mōkau River has signs of ecological stress.
Freshwater invertebrate MCI scores indicate ecological stress at some sites in all sub-catchments expect for Mokauiti-Aria, where nearly all sites had good MCI scores and two out of three sites had good fish scores. Mangaotaki-Mairoa also had two sites with good invertebrate scores.
The number of insect species detected from eDNA (an indicator for ecological health) were low to moderate, ranging between 20 to 40 species across the 7 sub-catchments. Mapiu stream, Mapara stream, Mangaotaki and Mokauiti streams had the highest number of insect species, while Mangaokowhai stream and the Upper Mōkau had the lowest number of insect species detected.
Native freshwater mussels, a rare invertebrate species and filter feeder, were detected in the sub-catchments of upper Mōkau, Mokauiti-Aria and the lower Mōkau.
The Mōkau river has a diverse fish community in the lower reaches (14 species), however, fish diversity is very low in the mid and upper reaches, consisting mainly of eels (longfin and shortfin) and brown trout.
Only one whitebait species was detected, Īnanga, in the lower reaches only.
Threatened fish species detected in the catchment include, lamprey, Īnanga, redfin bully, longfin eel and torrentfish.
Four species of introduced fish detected, mosquito fish, goldfish, brown trout and rainbow trout.
Barriers to fish migration in the Mōkau river, including manmade structures like dams and perched culverts and natural features like high waterfalls, will be restricting fish diversity.
The Mōkau River has at least two large manmade barriers to fish migration, the Mokauiti Dam and the Wairere Dam, and at least on large natural barrier, Omaru falls (45m high).
Many of our native species are excellent climbers, elvers can scale waterfalls up to 40 m high and kōaro even higher than this.
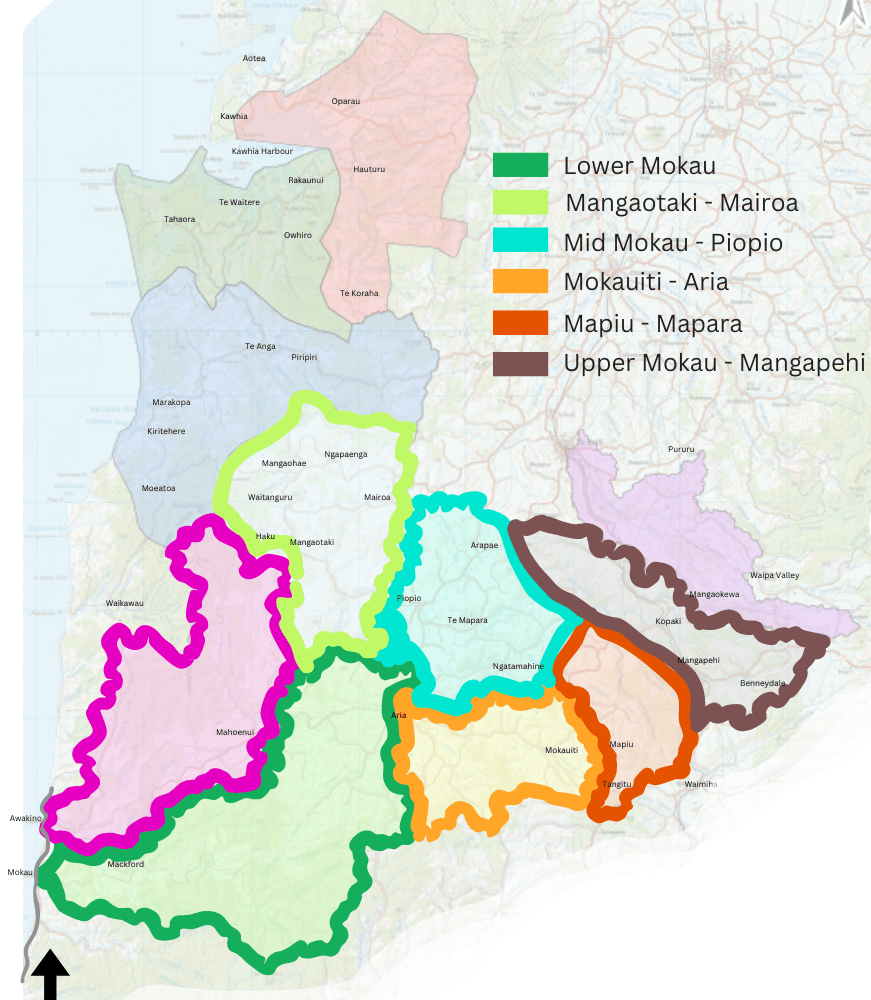
Mokau Sub Catchment Areas
2023 Quarterly Results
November 2023
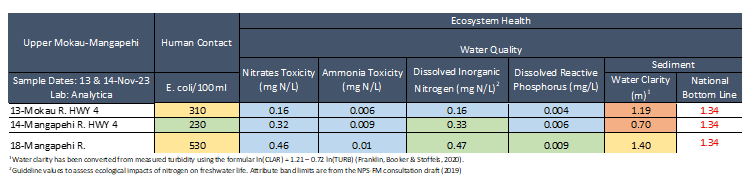
Overall, water quality on fair across Upper Mokau and Mangapehi in November.
E. coli concentrations was low at 14-Mangapehi River (230) and elevated at the other two sites (≥ 310). Nitrate concentrations were well below toxicity levels at all sites, being lowest at 13-Mokau R. HWY 4 (0.16 mg/L) and highest at 18-Mangapehi River (0.46 mg/L). Ammonia concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 0.01 mg/L). Dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations were good at all sites (≤ 0.47 mg/L). Dissolved reactive phosphorus concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 0.009 mg/L). Water clarity was fair (1.40 m) to poor at all sites (≤ 1.19 m), relative to the national bottom line (1.34 m).
Collection days: 13 & 14 November 2023
Mokau River – All sites in sub-catchment (November 2023)
Nutrient concentrations (nitrate, ammonia and dissolved reactive phosphorus) were low at most sites. Key contaminants were E. coli and water clarity.
E. coli: 56% of all sites had low concentrations (≤230), 25% had slightly elevated concentrations (between 280 - 530) and 19% had elevated concentrations (> 730). Nitrate and Ammonia: concentrations at 100% of sites were below toxicity levels (Nitrate ≤ 0.62 mg/L; Ammonia ≤ 0.02). Only one site had Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen (DIN) concentrations above 0.5 mg/L. Ecological impacts, including problematic growth of algae and/or aquatic plants and loss of sensitive aquatic species are likely to occur when DIN regularly exceeds 0.5 mg/L. Dissolved reactive phosphorus: 94% of sites had low concentrations (≤ 0.009 mg/L) and one site (16%) had slightly elevated concentrations (0.011 mg/L).Water clarity: 44% of sites had good water clarity (A or B band), two sites (13%) had reduced water clarity (C band) and 44% of sites had poor water clarity (D band). Bands for each site relate to the national bottom line (NBL) for water clarity and are dependent on landscape characteristics including geology, climate and elevation. The NBL for Mokau River’s monitoring sites are either 1.34 m or 0.61 m, dependant the local landscape characteristics.
September 2023
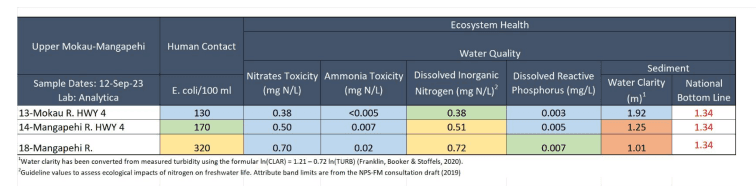
Overall, water quality on 12th September was fair to good. Suspended sediment was elevated at two out of three sites and E. coli and dissolved inorganic nitrogen were slightly elevated at some sites. E. coli concentrations were low at 2 out of 3 sites (≤ 170) and were elevated at 18-Mangapehi River (320). Nitrate concentrations were below toxicity levels at all sites being lowest at 13-Mokau R. HWY 4 (0.38 mg/L) and highest at 18-Mangapehi River (0.70 mg/L). Ammonia concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 0.02 mg/L). Two sites (14 and 18 on Mangapehi River) had dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations exceeding 0.5 mg/L, potentially impacting the health of the river. Dissolved reactive phosphorus concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 0.007 mg/L). Water clarity was very good at 13-Mokau R. HWY 4 and poor at all sites (≤ 1.25 m), relative to the national bottom line (1.34 m).
Collection date: 12 September 2023
Mokau River – All sites in all sub-catchments (September 2023)
Summary of water quality collected at 16 sites located across the Mokau River catchment sampled on 12th or 13th of September. E. coli: 63% of all sites had low concentrations (≤220), 25% had slightly elevated concentrations (between 270 - 380) and 13% of sites had elevated concentrations (> 550). Nitrate and Ammonia: 100% of sites had concentrations below toxicity levels (Nitrate ≤ 0.79 mg/L; Ammonia ≤ 0.09). However, 50% of sites had Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen (DIN) concentrations over 0.5 mg/L. Ecological impacts, including problematic growth of algae and/or aquatic plants and loss of sensitive aquatic species are likely when the combined concentration of DIN regularly exceed 0.5 mg/L. Dissolved reactive phosphorus: 94% of sites had low concentrations (≤ 0.009 mg/L) and one site (16%) had an elevated concentration (0.011 mg/L). Water clarity: 56% of sites had good water clarity (A or B band) and 44% of sites had poor clarity (D band). Bands for each site relate to the national bottom line for water clarity, which is either 1.34 m or 0.61 m, and is dependent on the local geology, climate and elevation.
May 2023
E. coli concentrations were low at 3 out of 4 sites (≤ 260) and were elevated at 18-Mangapehi River (310). Nitrate concentrations were below toxicity levels at all sites being lowest at 17-Paritikona Stream (0.40 mg/L) and highest at 14-Mangapehi River HWY 4 (0.70 mg/L). Ammonia concentrations were low at 3 sites (≤ 0.02 mg/L) and higher at 14-Mangapehi River HWY 4 (0.04 mg/L). Three out of four sites (all except 17-Paritikona Stream) had dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations exceeding 0.5 mg/L, potentially impacting the health of the river. Dissolved reactive phosphorus concentrations were low at all sites (≤ 0.008 mg/L). Water clarity was poor at all sites (≤ 0.71 m), relative to the national bottom line (1.34 m)
Sample date 8 & 14 May 2023.
Mokau River – All sites in all sub-catchments
This summarises the results collected across the Mokau River catchment from 27 sites sampled on either the 8th or 14th of May: E. coli: 58% of all sites had low concentrations (≤260) and 42% had slightly elevated concentrations (between 270 - 360). Nitrate and Ammonia: 100% of sites had concentrations below toxicity levels (Nitrate ≤ 2.39 mg/L; Ammonia ≤ 0.04). However, 67% of sites had Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen (DIN) concentrations over 0.5 mg/L. Ecological impacts, including problematic growth of algae and/or aquatic plants and loss of sensitive aquatic species are likely when the combined concentration of DIN regularly exceed 0.5 mg/L. Dissolved reactive phosphorus: 83% of sites had low concentrations (≤ 0.009 mg/L) and 17% of sites had elevated concentrations (0.011 – 0.017 mg/L). Water clarity: 8% of sites had good water clarity (A or B band), 8% had moderate clarity (C band) and 83% of sites had poor clarity (D band). Bands for each site relate to the national bottom line for water clarity, which is either 1.34 m or 0.61 m, and is dependent on the local geology, climate and elevation.
February 2023
Water Quality Summary 2022
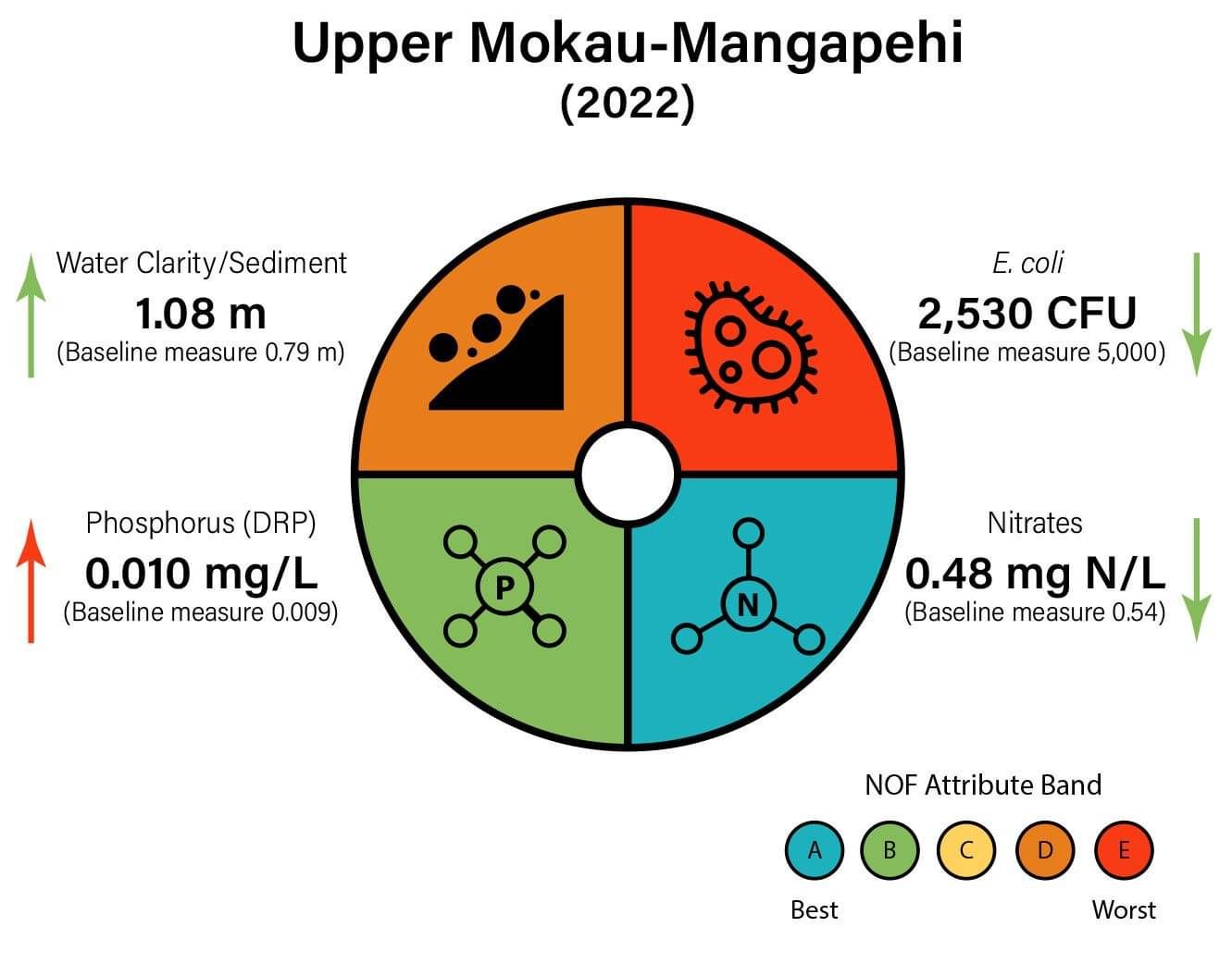
The water quality dial for Upper Mokau-Mangapehi combines data collected at 5 monitoring sites between January – December 2022, representing 28 individual samples. Nitrates and dissolved reactive phosphorus (DRP) were low. E. coli was elevated, while water clarity was low indicating elevated sediment loading. Arrows indicate an increase or decrease in values compared to the sub-catchment baseline (2015 – 2020). An increase in water clarity is positive for river health while an increase in all other attributes may impair river health.
2021 Summary
E. coli is the main contaminants of concern.
Dissolved Reactive Phosphorus is elevated at Mangaokewa Road – WRC site.
Site 13-Mokau R. HWY 4 had the best water quality and Mangaokewa Rd had the lowest water quality in 2021.
Attribute bands
A (or blue is the best) through to E (red) which is the worst.